The SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) is one of a number of cryptographic hash functions. A cryptographic hash is like a signature for a text or a data file. SHA-256 algorithm generates an almost-unique, fixed size 256-bit (32-byte) hash. Hash is a one way function – it cannot be decrypted back. This makes it suitable for password validation, challenge hash authentication, anti-tamper, digital signatures.
Usecases in Bitcoin
- Proof of Work algorithm in mining of bitcoins
- Creation of bitcoin addresses to improve security and privacy
Merkle‐Damgard construction
A method of building collision-resistant cryptographic hash functions from collision-resistant one-way compression functions. Hash functions take variable length input and always give an output of fixed length. Basically, there are three processing steps in Merkle-Damgard.
Padding step Padding is done so that the message length can be increased and equal length blocks can be formed of that. It creates an input whose size is a multiple of a fixed number (e.g. 512 or 1024) because compression functions cannot handle inputs of arbitrary size.
Divide into equal parts The hash function then divides the output of previous step with all the padding into equal size (m bit) blocks and processes them one at a time with a compression function, each time combining a block of the input with the output of the previous round.
Add padding block In order to make the construction secure the message is padded with a padding that encodes the length of the original message. This is called length padding or Merkle–Damgard strengthening.
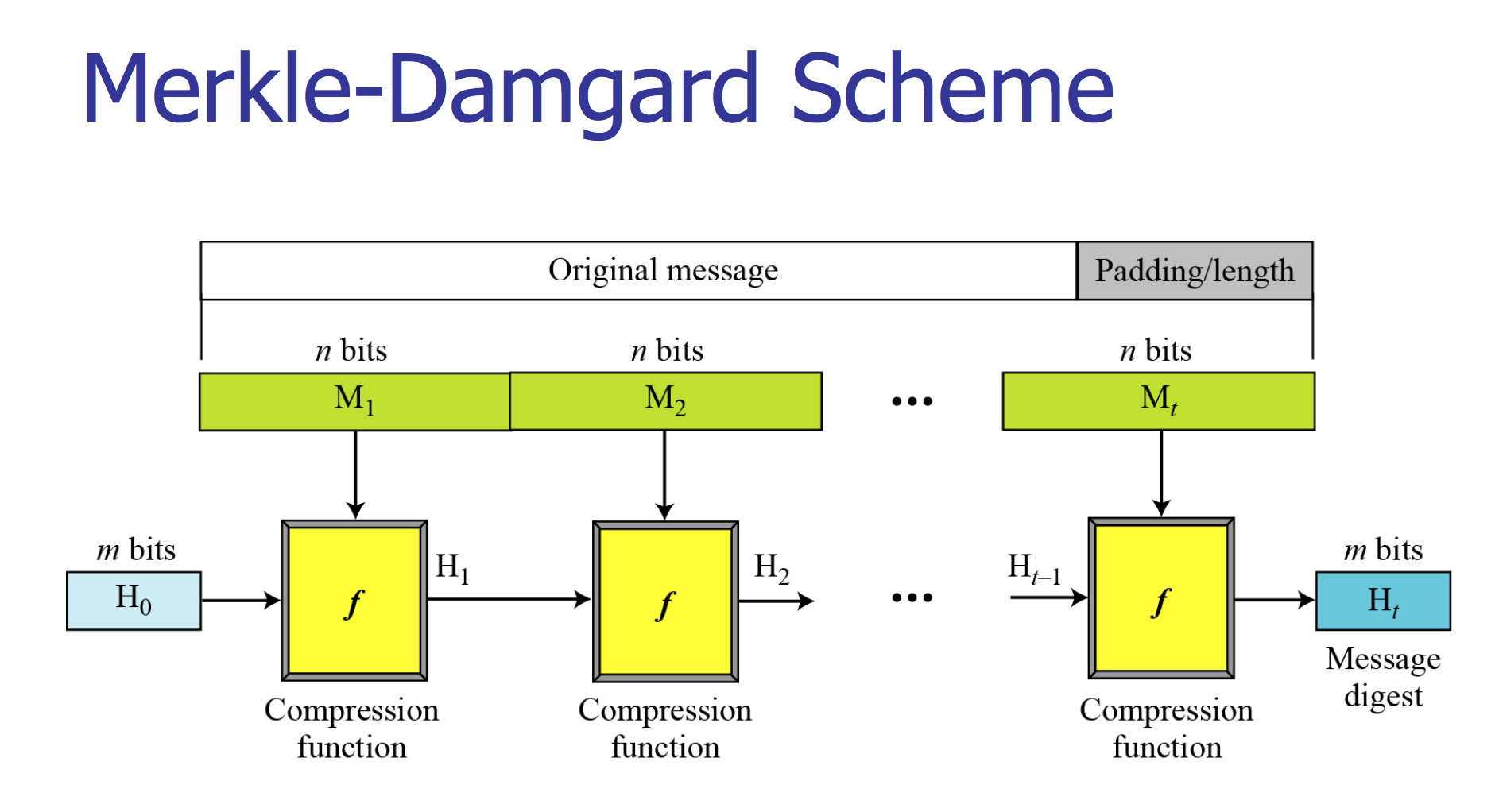
Here the compression function takes a fixed size input and is iterated a number of times where on each iteration:
- n-bit string is input
- m-bit string is output
- n > m
Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS)
US Secure Hash Algorithms (SHA and SHA-based HMAC and HKDF)